Your personal information can easily appear on Google Search through websites, directories, social media profiles, public records, or data broker platforms. Details like your phone number, email address, home address, photos, or other sensitive information may be visible to anyone searching your name. This can create privacy risks, unwanted contact, spam, identity theft concerns, or even reputation problems.
The good news is that Google provides several tools to help you remove or reduce personal information from search results. However, it is important to understand that Google does not host most content. It only shows links to websites. This means that in some cases, you may need to contact the website owner directly to remove the information from the source before it is completely removed from search results.
There are multiple ways to delete personal information from Google, including requesting removal directly from search results, using Google’s official removal forms, managing your personal data through the “Results about you” dashboard, removing outdated content, and requesting content removal from websites.
This guide explains the safest and easiest methods to remove your personal information step-by-step. Each method includes simple instructions that work on desktops, Android devices, and iPhones.
Why Personal Information Appears on Google?
In reality, Google is a search engine that indexes content available on websites across the internet. When your personal details appear in search results, it usually means that information already exists on a public webpage that Google has crawled and indexed.
Personal information often appears online through everyday activities. Creating social media profiles, registering on websites, listing business details, posting advertisements, or participating in forums can all make your information publicly accessible. If privacy settings are not properly configured, search engines may display this data when someone searches your name or contact details.
Another major source is data brokers and people-search websites. These platforms collect information from public records, marketing databases, and online sources. They then organize and publish personal profiles that may include addresses, phone numbers, relatives, or employment details. Many users are unaware that their data has been collected and listed until they find it on Google.
Government databases, court records, property records, and business registrations are often publicly accessible. When third-party websites aggregate these records, Google may index them, making the information easy to find through simple searches.
When users post job listings, rental ads, or business promotions, they often include phone numbers or email addresses. Even if the listing becomes outdated, the page may remain indexed for months or years.
Understanding the source is important because Google usually cannot remove information permanently unless the original website deletes or restricts the content.
Types of Information Google Can Remove:
Google does not remove all types of content, but it does allow the removal of certain personal and sensitive information that creates privacy or security risks. Removal requests are evaluated based on Google’s privacy policies, and approval depends on the nature of the content and its public value.
The most commonly approved category includes personal contact information shared without consent. This includes phone numbers, email addresses, and home addresses, especially when the information creates a risk of harassment, spam, or unwanted contact.
Financial and identity-related data are treated with higher priority. Bank account numbers, credit card details, government identification numbers, and confidential documents may qualify for urgent removal because they increase the risk of fraud or identity theft.
Google may also remove content that exposes personal information alongside harmful intent, such as doxxing, harassment campaigns, or malicious sharing. In such cases, the context and risk level are carefully reviewed before action is taken.
However, some information may not qualify for removal. Content that is part of news reporting, official public records, or government publications may remain visible if it serves public interest or legal transparency requirements.
| Eligible for Removal | Usually Not Removed |
|---|---|
| Phone numbers, emails, home addresses | News articles or media coverage |
| Bank or credit card information | Government public records |
| Identity numbers or confidential documents | Business information published officially |
| Personal data shared with malicious intent | Content widely public for public interest |
It is important to note that even when Google removes a search result, the information may still exist on the original website. For complete removal, users often need to contact the site owner directly.
How To Remove Your Information From Google
Whether your goal is to remove contact details, personal images, sensitive data, or unwanted search results, these methods will help you clean your online presence effectively and securely.
1. Remove Results Directly from Google Search
Google allows users to request the removal of personal information directly from search results. This method is best when sensitive details like phone numbers, addresses, or emails appear publicly.
It is quick and suitable for most privacy cases where the content violates Google’s personal information policies and requires manual review approval.
Step 1: Open Google Search and type your full name, phone number, email, or other personal details to locate exposed results easily.
Step 2: Now, identify the search result showing your private information and click the three dots icon beside the listing for options.
Step 3: From the information panel, select the ‘Remove result’ option to begin submitting a privacy removal request directly through Google.

Step 4: Then, choose the appropriate reason indicating that the result contains personal information, such as contact details, identity data, or sensitive content, publicly.
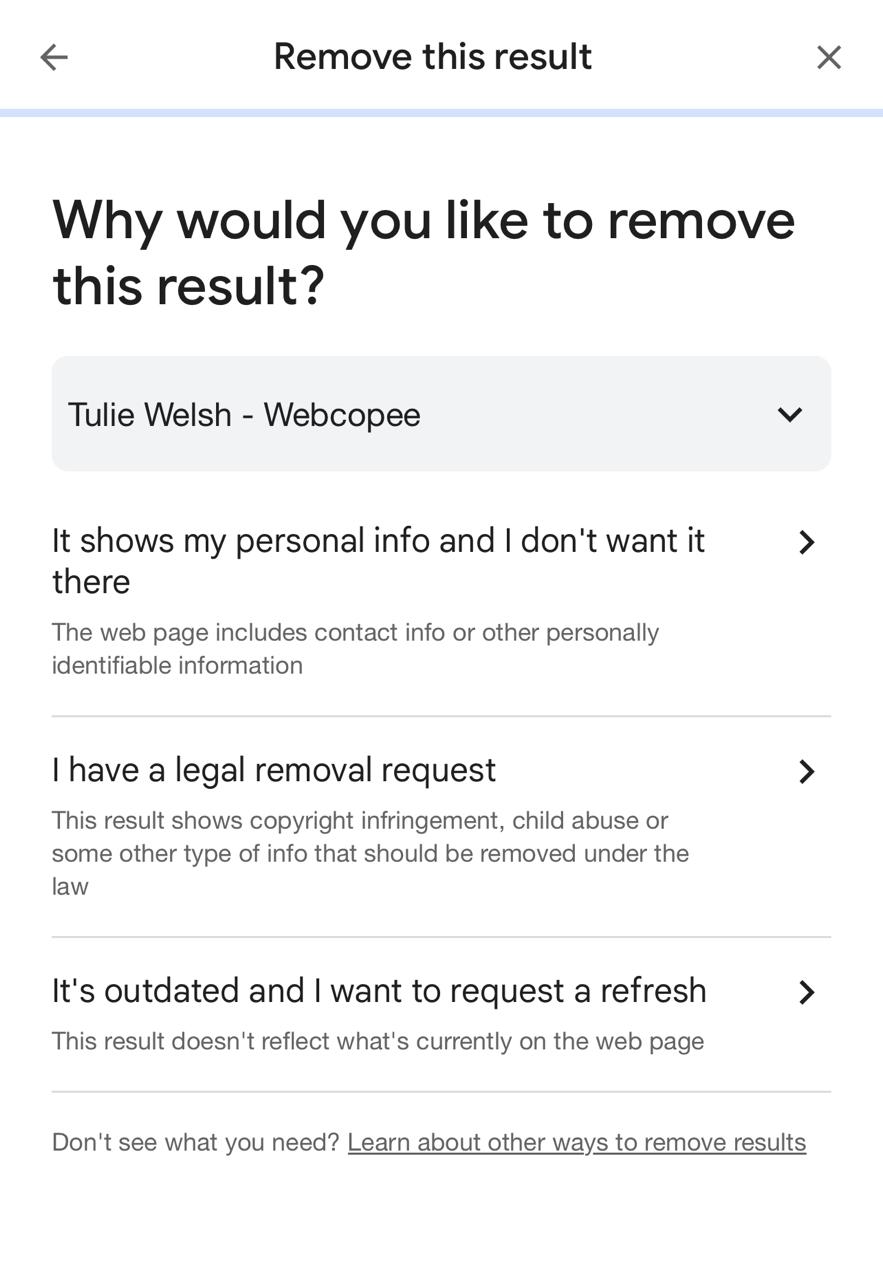
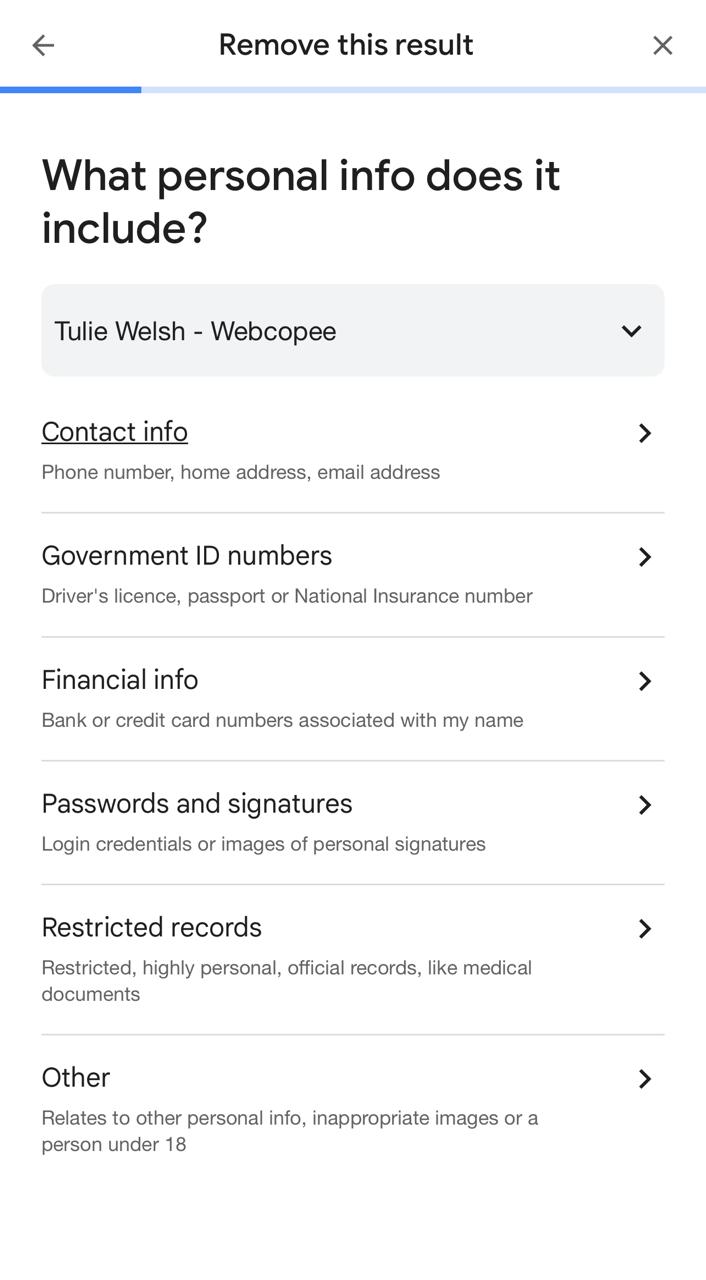
Step 5: Enter your contact information, review the request carefully, confirm accuracy, and submit the removal request for Google review processing officially.
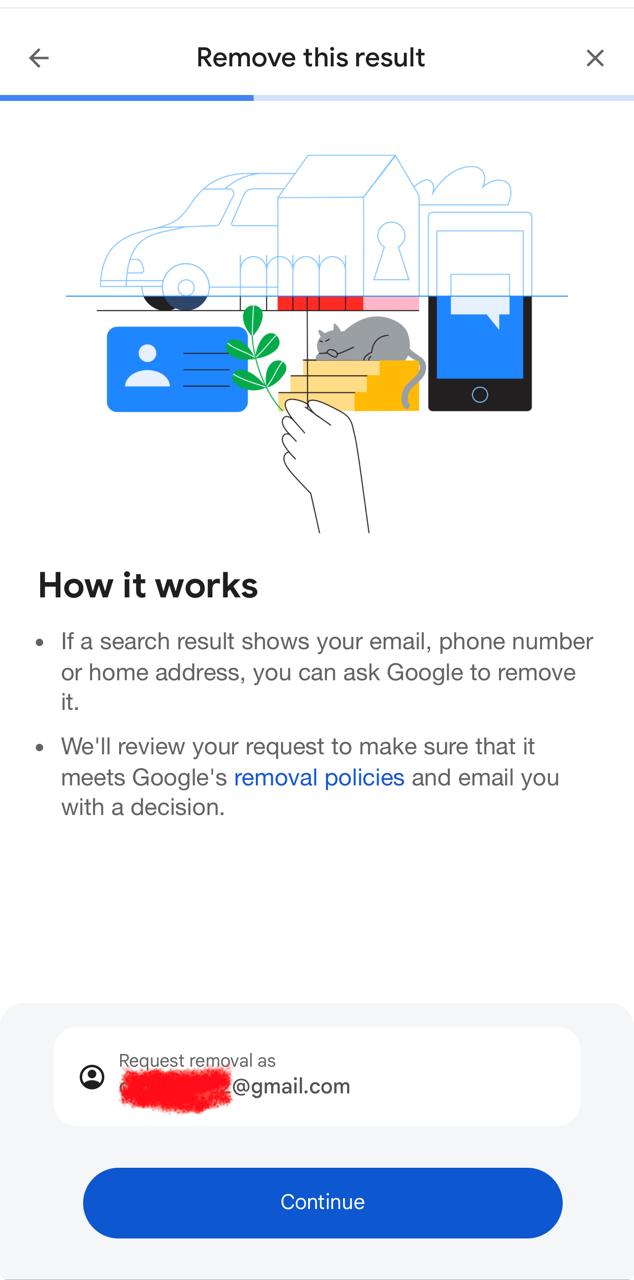
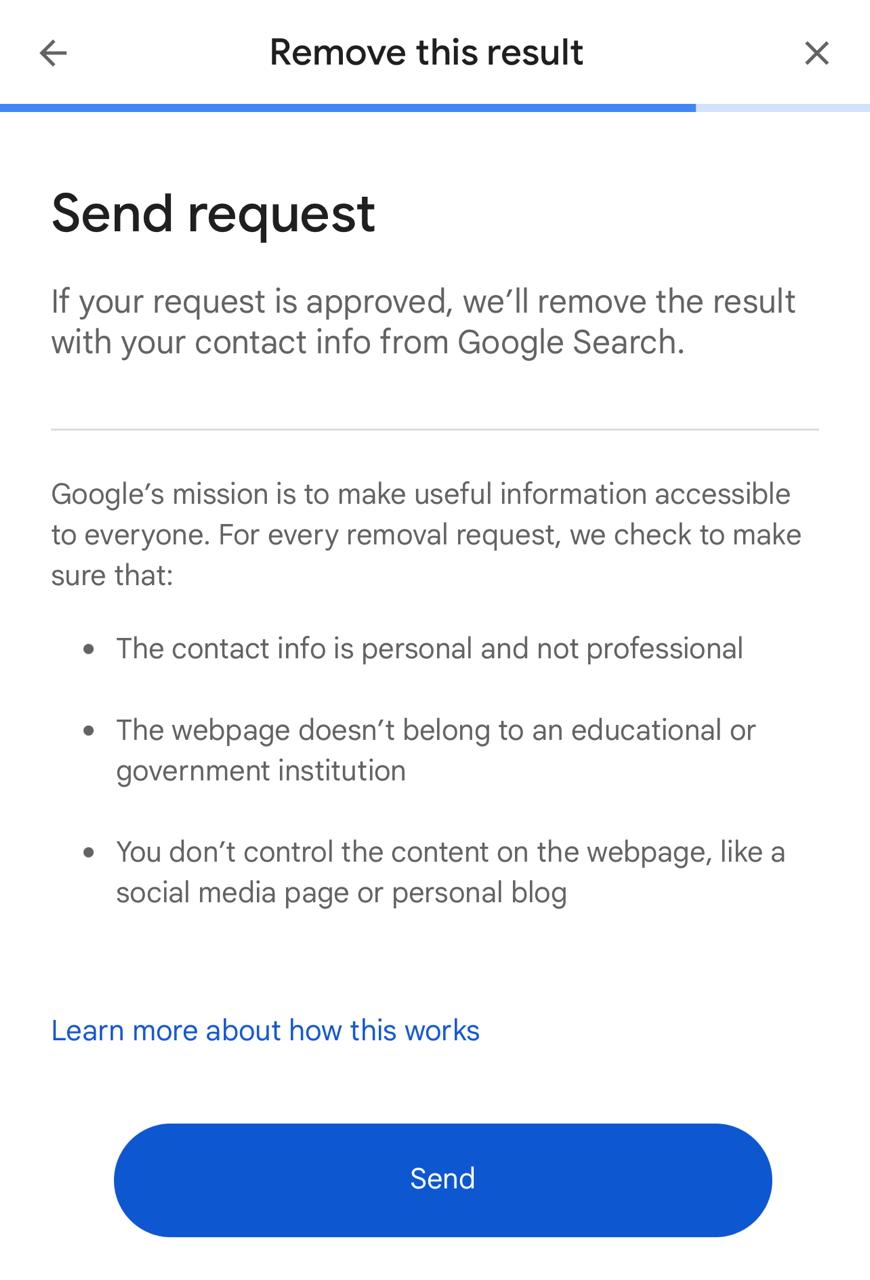
2. Submit Google Personal Information Removal Form
Google provides an official removal form for sensitive personal information appearing online. This method is useful for serious privacy risks such as financial data, identification numbers, or confidential details. Submitting accurate URLs and supporting information helps Google investigate faster and decide whether the content qualifies under their privacy policies.
Step 1: First of all, open the Personal Information Removal form to begin submitting a detailed privacy request online.
Step 2: Select the option stating content contains your personal information and choose your country to proceed with the eligibility questions.
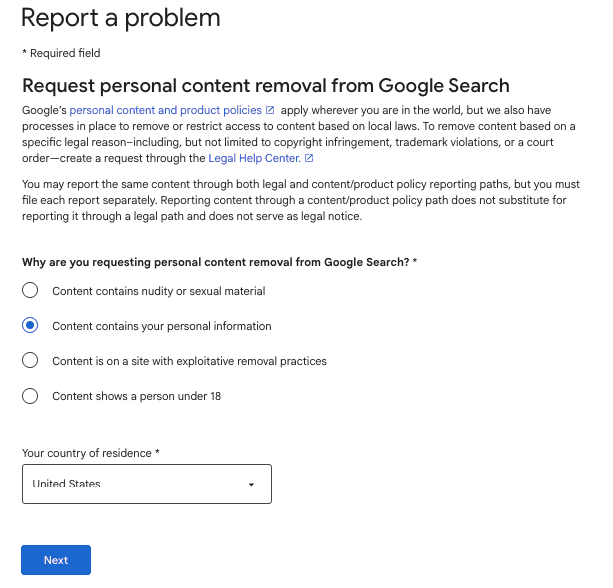
Step 3: Just specify the type of exposed information, such as address, identification number, financial data, or other sensitive personal details, accurately.
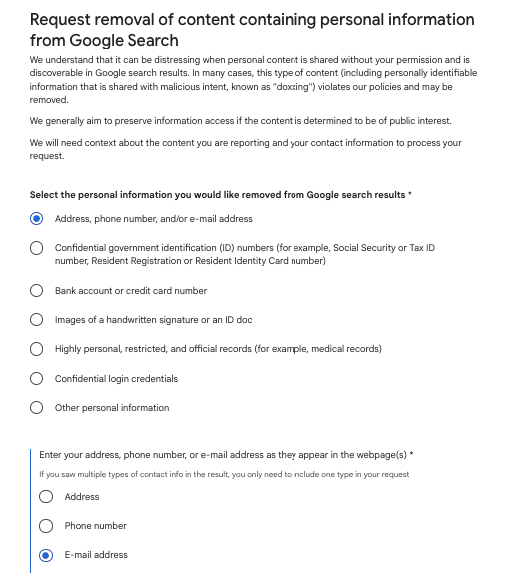
Step 4: Provide exact page URLs, search result links, search queries, and screenshots so Google can locate the information quickly and verify.

Step 5: Enter your contact details (i.e. email ID), agree to the terms, review the submission carefully, and send the request for Google’s privacy team evaluation process.
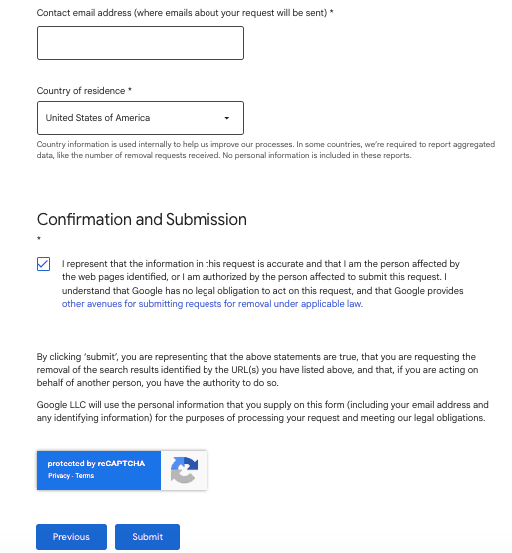
3. Use Results About You Dashboard
The Results About You dashboard helps monitor your personal contact information automatically. Google scans search results for matching details and alerts you when new exposures appear. This method allows users to request removals directly from a centralized monitoring and management tool easily.
Step 1: Sign in to your Google account and open the Results About You dashboard from privacy settings to start monitoring information.

Step 2: Click Get Started and enter personal details, including name, phone number, email address, and home address for scanning purposes.
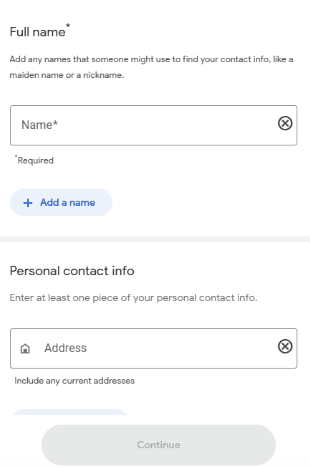
Step 3: Confirm that the information belongs to you and choose notification preferences such as email alerts or Google app push messages.
Step 4: Review detected matches inside the Results to Review section and check which search results display your personal information publicly.
Step 5: Select unwanted listings, click Request removal, and submit them for Google verification and removal consideration under privacy policy guidelines.
4. Request Removal from Website Owner
Removing personal information from the original website is the most effective long-term solution. Once deleted from the source, Google updates search results automatically. This method works best for directories, blogs, or data broker sites where your personal details are published without your permission or are unnecessarily outdated.
Step 1: Visit the webpage showing your personal information and locate the Contact, Support, Privacy, or Removal request section carefully for assistance.
Step 2: Now, explain and write a message requesting the removal of your personal data, explaining privacy concerns, and clearly identifying information belonging to you.
Step 3: Include exact page URLs, screenshots, and details about which content should be removed to help administrators process requests faster and more accurately.
Step 4: Request confirmation after removal so you can verify changes and ensure the information is no longer publicly accessible online.
Step 5: After deletion, submit a Google outdated content request if search results still display cached versions of removed information publicly.
How Long Removal Takes?
The time required to remove personal information from Google depends on the type of request, the accuracy of submitted details, and whether the content meets Google’s policy requirements. Some requests are processed quickly, while others require manual review and additional verification.
After submitting a removal request, Google typically sends a confirmation email. Automated checks may begin immediately, but cases involving personal information are usually reviewed by a privacy team. This review ensures that the request is valid, the information belongs to the requester, and the content qualifies for removal under policy guidelines.
In general, simple removal requests may take a few days to a few weeks. Requests involving sensitive data, legal considerations, or multiple URLs may take longer. If additional information is required, Google may contact the requester, which can extend the processing time.
If the original website removes the content, Google’s search index may update automatically during the next crawl. This process usually takes several days but can sometimes take a few weeks, depending on the website’s update frequency.
When Will Google Not Remove Content?
Google’s goal is to balance personal privacy with public access to information. Because of this, not all removal requests are approved. If content serves public interest, legal transparency, or informational value, Google may decide not to remove it.
Understanding these limitations helps users choose the correct approach, such as contacting the website owner, requesting corrections, or using privacy settings instead of relying only on Google removal tools.
TechniqueHow Removal Service
Data Cleanup
Remove Personal Data Online
We track sensitive details across search results, directories, and data brokers, then manage removal requests and ongoing privacy protection.
Request Removal
TechniqueHow Removal Service helps individuals reduce their online exposure by identifying, managing, and removing personal information from search engines and public websites. Many people struggle to locate all sources where their data appears, and manually removing it can be time-consuming. This service simplifies the process through structured analysis and professional handling.
Our specialists scan Google results, people-search platforms, directories, forums, and data broker websites to identify exposed personal information. This may include phone numbers, email addresses, home addresses, images, outdated profiles, or sensitive personal references.
After identifying exposure points, the service evaluates which items qualify for removal based on platform policies and privacy eligibility. Removal requests are then submitted to Google, website administrators, or data broker platforms, accompanied by proper documentation and follow-up.
One of the key advantages is ongoing monitoring. Personal information often reappears when databases update or new websites index old records. Regular monitoring helps detect new exposures early and allows quick removal actions before they spread widely.
| Stage | Action |
|---|---|
| Discovery | Identify personal information across search and websites |
| Evaluation | Check eligibility and privacy risk level |
| Removal | Submit requests to Google and source platforms |
| Monitoring | Track status and detect future exposures |
Public Records and Legal Limitations:
One of the biggest challenges in removing personal information from Google involves public records. Many types of personal data are legally considered public information. These records are created and maintained by government agencies for transparency, legal compliance, and public access. Because of this, neither Google nor most websites are required to remove such information unless specific legal conditions apply.
Public records may include court case details, property ownership records, business registrations, professional licenses, voter information, or government notices. Third-party websites often collect and publish these records in searchable formats. When Google indexes these pages, the information becomes easily accessible through name searches.
In most cases, Google will not remove content that comes directly from official government sources. This is because the information serves a public interest purpose. For example, legal judgments, bankruptcy filings, or company directorship details are meant to remain accessible for verification and transparency.
However, there are limited situations where removal or restriction may be possible. If a record has been sealed, expunged, or legally restricted by a court order, you may request the source website to update or remove it. Once the original content is removed or restricted, Google may update its search results accordingly.
| Record Type | Removal Possibility |
|---|---|
| Expunged or sealed court records | Possible after legal proof and source update |
| Incorrect or outdated public record copies | Possible by requesting website correction |
| Active court cases or government records | Usually not removable |
| Business registration or property ownership data | Generally not removable |
Case Examples and Use Scenarios:
Personal information removal needs vary depending on individual situations. Understanding common use cases helps users choose the right removal method and prioritize actions based on risk level and urgency.
One common scenario involves unwanted contact, and individuals often discover their phone numbers or email addresses listed on directories or old classified pages. This leads to spam calls, promotional messages, or unknown contacts. Removing these listings significantly reduces unwanted communication.
Another situation involves outdated professional or personal information. Old job listings, previous addresses, or inactive profiles may appear in search results and create confusion or credibility issues. Cleaning outdated content helps maintain an accurate digital identity.
Individuals may want to remove old posts, negative mentions, or irrelevant content that affects their personal or professional image. While not all content qualifies for removal, outdated or privacy-sensitive items can often be reduced or de-indexed.
Privacy protection is especially important for individuals facing harassment, stalking concerns, or safety risks. In such cases, removing home addresses, personal photos, or family details becomes a priority.
Conclusion:
Managing your personal information on Google is an important step toward protecting your privacy and maintaining control over your online identity. Since search engines reflect information already available on the internet, effective removal usually involves both Google requests and action at the source website.
There are several reliable methods available, including direct search result removal, official privacy forms, the Results About You dashboard, outdated content tools, and contacting website owners. When used correctly, these methods can significantly reduce the visibility of sensitive or unwanted personal information.
However, it is equally important to understand the limitations. Content related to public records, news reporting, or legal transparency may not be removable. In such cases, users may need to focus on updating information, limiting exposure, or improving privacy settings instead of complete deletion.
Professional support services, such as structured removal and monitoring solutions, can simplify the process for individuals who want comprehensive protection without managing multiple requests manually.
Frequently Asked Questions:
No, you cannot completely remove your name from Google unless all websites containing your name delete the information. Google only shows links to existing web content. If your name appears on multiple websites, you must request removal from each source. Once the content is deleted or restricted, Google will gradually update search results. Using Google removal tools helps reduce visibility, but full removal depends on the original websites.
It is recommended to review your online presence at least once every few months. Regular searches of your name, phone number, and email help identify new exposures early. Data broker sites and directories frequently update their databases, which may republish old information. Using Google Alerts or the Results About You dashboard can automate monitoring and notify you when your personal details appear in new search results.
To prevent reappearance, first remove your contact details from the original website or platform where they were published. Then adjust privacy settings on social media, business listings, and online profiles to restrict public visibility. Avoid posting personal contact details on public forums or classified websites. You should also regularly search for your information or enable monitoring tools so you can quickly remove any new exposures before they spread.
